简介
文章 Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation using Part Affinity Fields
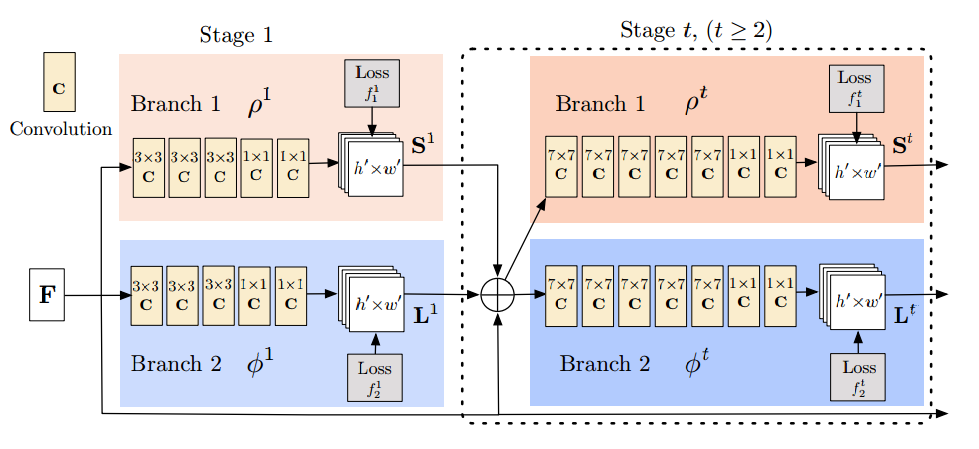
首先由一个基础网络获取高层共享特征F, 然后分多个stage来编码key point heatmap(S)和Part Affinity Fields (L)。文章的精华是PAF的设计和使用
下面通过代码来解释
import argparse
import cv2
import math
import time
import numpy as np
import util
from config_reader import config_reader
from scipy.ndimage.filters import gaussian_filter
from model import get_testing_model
#这里比较重要,这些参数limbSeq表示heatmap里面每层代表的是哪个关节点,哪两层的连接是组成的limb,每个limb的PAF向量方向是由mapIdx对应的两层表示(x,y)
# find connection in the specified sequence, center 29 is in the position 15
limbSeq = [[2, 3], [2, 6], [3, 4], [4, 5], [6, 7], [7, 8], [2, 9], [9, 10], \
[10, 11], [2, 12], [12, 13], [13, 14], [2, 1], [1, 15], [15, 17], \
[1, 16], [16, 18], [3, 17], [6, 18]]
# the middle joints heatmap correpondence
mapIdx = [[31, 32], [39, 40], [33, 34], [35, 36], [41, 42], [43, 44], [19, 20], [21, 22], \
[23, 24], [25, 26], [27, 28], [29, 30], [47, 48], [49, 50], [53, 54], [51, 52], \
[55, 56], [37, 38], [45, 46]]
# visualize
colors = [[255, 0, 0], [255, 85, 0], [255, 170, 0], [255, 255, 0], [170, 255, 0], [85, 255, 0],
[0, 255, 0], \
[0, 255, 85], [0, 255, 170], [0, 255, 255], [0, 170, 255], [0, 85, 255], [0, 0, 255],
[85, 0, 255], \
[170, 0, 255], [255, 0, 255], [255, 0, 170], [255, 0, 85]]
def process (input_image, params, model_params):
oriImg = cv2.imread(input_image) # B,G,R order
# 获取不同的缩放比例
multiplier = [x * model_params['boxsize'] / oriImg.shape[0] for x in params['scale_search']]
# 18个关节点加1个背景
heatmap_avg = np.zeros((oriImg.shape[0], oriImg.shape[1], 19))
# 19个肢体的单位向量方向,其中最后两个肢体不在躯干上,所以最后显示忽略
paf_avg = np.zeros((oriImg.shape[0], oriImg.shape[1], 38))
#获取不同尺度下heatmap和PAF的平均值
for m in range(len(multiplier)):
scale = multiplier[m]
imageToTest = cv2.resize(oriImg, (0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
imageToTest_padded, pad = util.padRightDownCorner(imageToTest, model_params['stride'],
model_params['padValue'])
input_img = np.transpose(np.float32(imageToTest_padded[:,:,:,np.newaxis]), (3,0,1,2)) # required shape (1, width, height, channels)
output_blobs = model.predict(input_img)
# extract outputs, resize, and remove padding
heatmap = np.squeeze(output_blobs[1]) # output 1 is heatmaps
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap, (0, 0), fx=model_params['stride'], fy=model_params['stride'],
interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
heatmap = heatmap[:imageToTest_padded.shape[0] - pad[2], :imageToTest_padded.shape[1] - pad[3],
:]
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap, (oriImg.shape[1], oriImg.shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
paf = np.squeeze(output_blobs[0]) # output 0 is PAFs
paf = cv2.resize(paf, (0, 0), fx=model_params['stride'], fy=model_params['stride'],
interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
paf = paf[:imageToTest_padded.shape[0] - pad[2], :imageToTest_padded.shape[1] - pad[3], :]
paf = cv2.resize(paf, (oriImg.shape[1], oriImg.shape[0]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
heatmap_avg = heatmap_avg + heatmap / len(multiplier)
paf_avg = paf_avg + paf / len(multiplier)
all_peaks = []
peak_counter = 0
#寻找每个关节点的位置,关节点需要满足该点的confidence大于四周每个点
for part in range(18):
map_ori = heatmap_avg[:, :, part]
map = gaussian_filter(map_ori, sigma=3)
map_left = np.zeros(map.shape)
map_left[1:, :] = map[:-1, :]
map_right = np.zeros(map.shape)
map_right[:-1, :] = map[1:, :]
map_up = np.zeros(map.shape)
map_up[:, 1:] = map[:, :-1]
map_down = np.zeros(map.shape)
map_down[:, :-1] = map[:, 1:]
peaks_binary = np.logical_and.reduce(
(map >= map_left, map >= map_right, map >= map_up, map >= map_down, map > params['thre1']))
peaks = list(zip(np.nonzero(peaks_binary)[1], np.nonzero(peaks_binary)[0])) # note reverse
peaks_with_score = [x + (map_ori[x[1], x[0]],) for x in peaks]
id = range(peak_counter, peak_counter + len(peaks))
peaks_with_score_and_id = [peaks_with_score[i] + (id[i],) for i in range(len(id))]
all_peaks.append(peaks_with_score_and_id)
peak_counter += len(peaks)
connection_all = []
special_k = []
mid_num = 10
#匹配相连接的关节点组成的肢体,在关节点连线上用10个点的采样替代该连线上的积分,当满足肢体上点方向一致,得分满足条件时,将该肢体参数保留
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
score_mid = paf_avg[:, :, [x - 19 for x in mapIdx[k]]]
candA = all_peaks[limbSeq[k][0] - 1]
candB = all_peaks[limbSeq[k][1] - 1]
nA = len(candA)
nB = len(candB)
indexA, indexB = limbSeq[k]
if (nA != 0 and nB != 0):
connection_candidate = []
for i in range(nA):
for j in range(nB):
vec = np.subtract(candB[j][:2], candA[i][:2])
norm = math.sqrt(vec[0] * vec[0] + vec[1] * vec[1])
# failure case when 2 body parts overlaps
if norm == 0:
continue
vec = np.divide(vec, norm)
startend = list(zip(np.linspace(candA[i][0], candB[j][0], num=mid_num), \
np.linspace(candA[i][1], candB[j][1], num=mid_num)))
vec_x = np.array(
[score_mid[int(round(startend[I][1])), int(round(startend[I][0])), 0] \
for I in range(len(startend))])
vec_y = np.array(
[score_mid[int(round(startend[I][1])), int(round(startend[I][0])), 1] \
for I in range(len(startend))])
score_midpts = np.multiply(vec_x, vec[0]) + np.multiply(vec_y, vec[1])
score_with_dist_prior = sum(score_midpts) / len(score_midpts) + min(
0.5 * oriImg.shape[0] / norm - 1, 0)
criterion1 = len(np.nonzero(score_midpts > params['thre2'])[0]) > 0.8 * len(
score_midpts)
criterion2 = score_with_dist_prior > 0
if criterion1 and criterion2:
connection_candidate.append([i, j, score_with_dist_prior,
score_with_dist_prior + candA[i][2] + candB[j][2]])
#通过排序找寻最匹配的关节点连线肢体,找寻的肢体个数不大于关节点的个数。
connection_candidate = sorted(connection_candidate, key=lambda x: x[2], reverse=True)
connection = np.zeros((0, 5))
for c in range(len(connection_candidate)):
i, j, s = connection_candidate[c][0:3]
#每个关节点只属于一个肢体
if (i not in connection[:, 3] and j not in connection[:, 4]):
connection = np.vstack([connection, [candA[i][3], candB[j][3], s, i, j]])
if (len(connection) >= min(nA, nB)):
break
connection_all.append(connection)
else:
#表示没有找到关节点对匹配的肢体
special_k.append(k)
connection_all.append([])
# last number in each row is the total parts number of that person
# the second last number in each row is the score of the overall configuration
subset = -1 * np.ones((0, 20))
candidate = np.array([item for sublist in all_peaks for item in sublist])
#肢体连接策略
#对于某个肢体
for k in range(len(mapIdx)):
if k not in special_k:
#配对关节点A和B组成的肢体
partAs = connection_all[k][:, 0]
partBs = connection_all[k][:, 1]
indexA, indexB = np.array(limbSeq[k]) - 1
for i in range(len(connection_all[k])): # = 1:size(temp,1)
found = 0
subset_idx = [-1, -1]
for j in range(len(subset)): # 1:size(subset,1):
if subset[j][indexA] == partAs[i] or subset[j][indexB] == partBs[i]:
subset_idx[found] = j
found += 1
#如果肢体组成的关节点A,B有一端连接到某个人体则将该肢体给某个人体
if found == 1:
j = subset_idx[0]
if (subset[j][indexB] != partBs[i]):
subset[j][indexB] = partBs[i]
subset[j][-1] += 1
subset[j][-2] += candidate[partBs[i].astype(int), 2] + connection_all[k][i][2]
#如果肢体组成的关节点A,B分别连到了两个人体,则表明这两个人体应该组成一个人体,则合并两个人体(当肢体是按顺序拼接情况下不存在这样的状况)
elif found == 2: # if found 2 and disjoint, merge them
j1, j2 = subset_idx
membership = ((subset[j1] >= 0).astype(int) + (subset[j2] >= 0).astype(int))[:-2]
if len(np.nonzero(membership == 2)[0]) == 0: # merge
subset[j1][:-2] += (subset[j2][:-2] + 1)
subset[j1][-2:] += subset[j2][-2:]
subset[j1][-2] += connection_all[k][i][2]
subset = np.delete(subset, j2, 0)
else: # as like found == 1
subset[j1][indexB] = partBs[i]
subset[j1][-1] += 1
subset[j1][-2] += candidate[partBs[i].astype(int), 2] + connection_all[k][i][2]
# if find no partA in the subset, create a new subset
#如果肢体组成的关节点A,B没有被连接到某个人体则组成新的人体
elif not found and k < 17:
row = -1 * np.ones(20)
row[indexA] = partAs[i]
row[indexB] = partBs[i]
row[-1] = 2
row[-2] = sum(candidate[connection_all[k][i, :2].astype(int), 2]) + \
connection_all[k][i][2]
subset = np.vstack([subset, row])
# delete some rows of subset which has few parts occur
deleteIdx = [];
for i in range(len(subset)):
if subset[i][-1] < 4 or subset[i][-2] / subset[i][-1] < 0.4:
deleteIdx.append(i)
subset = np.delete(subset, deleteIdx, axis=0)
canvas = cv2.imread(input_image) # B,G,R order
for i in range(18):
for j in range(len(all_peaks[i])):
cv2.circle(canvas, all_peaks[i][j][0:2], 4, colors[i], thickness=-1)
stickwidth = 4
for i in range(17):
for n in range(len(subset)):
index = subset[n][np.array(limbSeq[i]) - 1]
if -1 in index:
continue
cur_canvas = canvas.copy()
Y = candidate[index.astype(int), 0]
X = candidate[index.astype(int), 1]
mX = np.mean(X)
mY = np.mean(Y)
length = ((X[0] - X[1]) ** 2 + (Y[0] - Y[1]) ** 2) ** 0.5
angle = math.degrees(math.atan2(X[0] - X[1], Y[0] - Y[1]))
polygon = cv2.ellipse2Poly((int(mY), int(mX)), (int(length / 2), stickwidth), int(angle), 0,
360, 1)
cv2.fillConvexPoly(cur_canvas, polygon, colors[i])
canvas = cv2.addWeighted(canvas, 0.4, cur_canvas, 0.6, 0)
return canvas
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 设置资源路径
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--image', type=str, required=True, help='input image')
parser.add_argument('--output', type=str, default='result.png', help='output image')
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='model/keras/model.h5', help='path to the weights file')
args = parser.parse_args()
input_image = args.image
output = args.output
keras_weights_file = args.model
# load model
# authors of original model don't use
# vgg normalization (subtracting mean) on input images
model = get_testing_model()
model.load_weights(keras_weights_file)
# load config
params, model_params = config_reader()
print('start processing...')
tic = time.time()
# generate image with body parts
canvas = process(input_image, params, model_params)
toc = time.time()
print ('processing time is %.5f' % (toc - tic))
cv2.imwrite(output, canvas)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
看我写的辛苦求打赏啊!!!有学术讨论和指点请加微信manutdzou,注明