use ubuntu caffe as libs
使用CMake project来外部编译需要调用caffe库的独立项目
git clone https://github.com/BVLC/caffe.git
cd caffe && mkdir cmake_build && cd cmake_build
cmake .. -DBUILD_SHARED_LIB=ON
cmake . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug # switch to debug
make -j 12 && make install # installs by default to build_dir/install
cmake . -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release # switch to release
make -j 12 && make install # doesn’t overwrite debug install
编译完成以后,就可以利用cmake把caffe和独立的C++项目链接
cmake脚本模板如下
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.8)
find_package(Caffe)
include_directories(${Caffe_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_definitions(${Caffe_DEFINITIONS}) # ex. -DCPU_ONLY
add_executable(caffeinated_application main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(caffeinated_application ${Caffe_LIBRARIES})
这个模板可以直接使用main.cpp链接caffe库生成可执行文件
基于caffe库提供一个动态库供第三方程序调用功能接口
假设我们要向第三方程序提供基于caffe的功能函数
文件结构如下
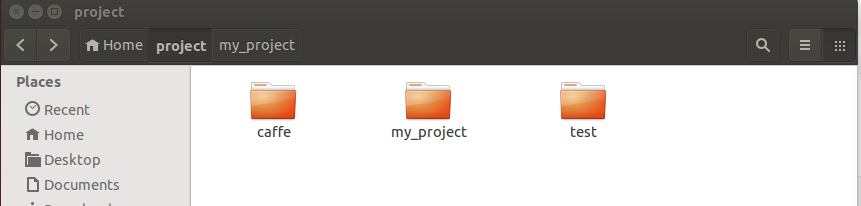
caffe文件夹是上面用cmake编译的第三方库,my_project是对应的项目文件夹,文件结构如下:
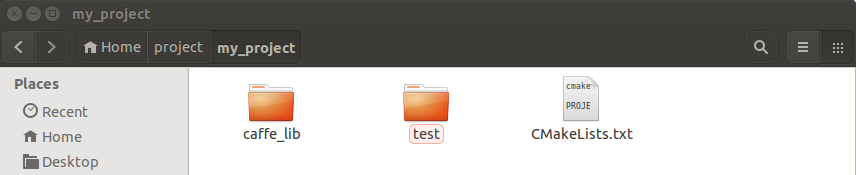
caffe_lib中是我们提供的动态库,test里面是外部调用程序,首先编写my_project的CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.8)
PROJECT(Test)
#要显示执行构建过程中详细的信息(比如为了得到更详细的出错信息)
SET( CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON )
#添加子目录
ADD_SUBDIRECTORY(caffe_lib)
ADD_SUBDIRECTORY(test)
caffe_lib中的source用于生成基于caffe的动态链接库
classification.h里面内容
#include <caffe/caffe.hpp>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iosfwd>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
#ifdef USE_OPENCV
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#endif // USE_OPENCV
using namespace caffe; // NOLINT(build/namespaces)
using std::string;
/* Pair (label, confidence) representing a prediction. */
typedef std::pair<string, float> Prediction;
class Classifier {
public:
Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file);
std::vector<Prediction> Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N = 5);
private:
void SetMean(const string& mean_file);
std::vector<float> Predict(const cv::Mat& img);
void WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
void Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels);
private:
shared_ptr<Net<float> > net_;
cv::Size input_geometry_;
int num_channels_;
cv::Mat mean_;
std::vector<string> labels_;
};
static bool PairCompare(const std::pair<float, int>& lhs,
const std::pair<float, int>& rhs);
static std::vector<int> Argmax(const std::vector<float>& v, int N);
std::vector<Prediction> classification(string model_file,string trained_file,string mean_file,string label_file,string file);
classification.cpp里面内容
#include "classification.h"
#ifdef USE_OPENCV
Classifier::Classifier(const string& model_file,
const string& trained_file,
const string& mean_file,
const string& label_file) {
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::CPU);
#else
Caffe::set_mode(Caffe::GPU);
#endif
/* Load the network. */
net_.reset(new Net<float>(model_file, TEST));
net_->CopyTrainedLayersFrom(trained_file);
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_inputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one input.";
CHECK_EQ(net_->num_outputs(), 1) << "Network should have exactly one output.";
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
num_channels_ = input_layer->channels();
CHECK(num_channels_ == 3 || num_channels_ == 1)
<< "Input layer should have 1 or 3 channels.";
input_geometry_ = cv::Size(input_layer->width(), input_layer->height());
/* Load the binaryproto mean file. */
SetMean(mean_file);
/* Load labels. */
std::ifstream labels(label_file.c_str());
CHECK(labels) << "Unable to open labels file " << label_file;
string line;
while (std::getline(labels, line))
labels_.push_back(string(line));
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
CHECK_EQ(labels_.size(), output_layer->channels())
<< "Number of labels is different from the output layer dimension.";
}
static bool PairCompare(const std::pair<float, int>& lhs,
const std::pair<float, int>& rhs) {
return lhs.first > rhs.first;
}
/* Return the indices of the top N values of vector v. */
static std::vector<int> Argmax(const std::vector<float>& v, int N) {
std::vector<std::pair<float, int> > pairs;
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
pairs.push_back(std::make_pair(v[i], i));
std::partial_sort(pairs.begin(), pairs.begin() + N, pairs.end(), PairCompare);
std::vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
result.push_back(pairs[i].second);
return result;
}
/* Return the top N predictions. */
std::vector<Prediction> Classifier::Classify(const cv::Mat& img, int N) {
std::vector<float> output = Predict(img);
N = std::min<int>(labels_.size(), N);
std::vector<int> maxN = Argmax(output, N);
std::vector<Prediction> predictions;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
int idx = maxN[i];
predictions.push_back(std::make_pair(labels_[idx], output[idx]));
}
return predictions;
}
/* Load the mean file in binaryproto format. */
void Classifier::SetMean(const string& mean_file) {
BlobProto blob_proto;
ReadProtoFromBinaryFileOrDie(mean_file.c_str(), &blob_proto);
/* Convert from BlobProto to Blob<float> */
Blob<float> mean_blob;
mean_blob.FromProto(blob_proto);
CHECK_EQ(mean_blob.channels(), num_channels_)
<< "Number of channels of mean file doesn't match input layer.";
/* The format of the mean file is planar 32-bit float BGR or grayscale. */
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
float* data = mean_blob.mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < num_channels_; ++i) {
/* Extract an individual channel. */
cv::Mat channel(mean_blob.height(), mean_blob.width(), CV_32FC1, data);
channels.push_back(channel);
data += mean_blob.height() * mean_blob.width();
}
/* Merge the separate channels into a single image. */
cv::Mat mean;
cv::merge(channels, mean);
/* Compute the global mean pixel value and create a mean image
* filled with this value. */
cv::Scalar channel_mean = cv::mean(mean);
mean_ = cv::Mat(input_geometry_, mean.type(), channel_mean);
}
std::vector<float> Classifier::Predict(const cv::Mat& img) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
input_layer->Reshape(1, num_channels_,
input_geometry_.height, input_geometry_.width);
/* Forward dimension change to all layers. */
net_->Reshape();
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels;
WrapInputLayer(&input_channels);
Preprocess(img, &input_channels);
net_->Forward();
/* Copy the output layer to a std::vector */
Blob<float>* output_layer = net_->output_blobs()[0];
const float* begin = output_layer->cpu_data();
const float* end = begin + output_layer->channels();
return std::vector<float>(begin, end);
}
/* Wrap the input layer of the network in separate cv::Mat objects
* (one per channel). This way we save one memcpy operation and we
* don't need to rely on cudaMemcpy2D. The last preprocessing
* operation will write the separate channels directly to the input
* layer. */
void Classifier::WrapInputLayer(std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
Blob<float>* input_layer = net_->input_blobs()[0];
int width = input_layer->width();
int height = input_layer->height();
float* input_data = input_layer->mutable_cpu_data();
for (int i = 0; i < input_layer->channels(); ++i) {
cv::Mat channel(height, width, CV_32FC1, input_data);
input_channels->push_back(channel);
input_data += width * height;
}
}
void Classifier::Preprocess(const cv::Mat& img,
std::vector<cv::Mat>* input_channels) {
/* Convert the input image to the input image format of the network. */
cv::Mat sample;
if (img.channels() == 3 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 1)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2GRAY);
else if (img.channels() == 4 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_BGRA2BGR);
else if (img.channels() == 1 && num_channels_ == 3)
cv::cvtColor(img, sample, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
else
sample = img;
cv::Mat sample_resized;
if (sample.size() != input_geometry_)
cv::resize(sample, sample_resized, input_geometry_);
else
sample_resized = sample;
cv::Mat sample_float;
if (num_channels_ == 3)
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC3);
else
sample_resized.convertTo(sample_float, CV_32FC1);
cv::Mat sample_normalized;
cv::subtract(sample_float, mean_, sample_normalized);
/* This operation will write the separate BGR planes directly to the
* input layer of the network because it is wrapped by the cv::Mat
* objects in input_channels. */
cv::split(sample_normalized, *input_channels);
CHECK(reinterpret_cast<float*>(input_channels->at(0).data)
== net_->input_blobs()[0]->cpu_data())
<< "Input channels are not wrapping the input layer of the network.";
}
#endif // USE_OPENCV
std::vector<Prediction> classification(string model_file,string trained_file,string mean_file,string label_file,string file) {
Classifier classifier(model_file, trained_file, mean_file, label_file);
std::cout << "---------- Prediction for "
<< file << " ----------" << std::endl;
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(file, -1);
CHECK(!img.empty()) << "Unable to decode image " << file;
std::vector<Prediction> predictions = classifier.Classify(img);
return predictions;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.8)
MESSAGE(STATUS "This is caffe_lib_SOURCE_DIR="${caffe_lib_SOURCE_DIR})
MESSAGE(STATUS "This is CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR="${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR})
#set(caffe_lib_srcs classification.cpp)
#set(caffe_lib_hdrs classification.h)
#用于将当前目录下的所有源文件的名字保存在变量 LIB_SRC 中
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(. LIB_SRC)
#把编译出来的库文件输出到项目的lib目录下
#例如运行“cmake ..”的目录为build,则在build/lib目录下生成
SET(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
add_library(classification_lib SHARED ${LIB_SRC})
find_package(Caffe)
if(Caffe_FOUND)
#添加头文件搜索路径
include_directories(${Caffe_INCLUDE_DIRS})
add_definitions(${Caffe_DEFINITIONS})
set_target_properties(classification_lib PROPERTIES output_name "classification_lib")
target_link_libraries(classification_lib ${Caffe_LIBRARIES})
else(Caffe_FOUND)
MESSAGE(FATAL_ERROR "Caffe library not found")
endif(Caffe_FOUND)
test中的source用于测试调用动态链接库
test.cpp
#include "classification.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
if (argc != 6) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0]
<< " deploy.prototxt network.caffemodel"
<< " mean.binaryproto labels.txt img.jpg" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
::google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
string model_file = argv[1];
string trained_file = argv[2];
string mean_file = argv[3];
string label_file = argv[4];
string file = argv[5];
std::vector<Prediction> predictions = classification(model_file,trained_file,mean_file,label_file,file);
/* Print the top N predictions. */
for (size_t i = 0; i < predictions.size(); ++i) {
Prediction p = predictions[i];
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4) << p.second << " - \""
<< p.first << "\"" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
#把编译出来的可执行文件输出到项目的bin目录下
#例如运行“cmake ..”的目录为build,则在build/bin目录下生成
SET(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/bin)
find_package(Caffe)
if(Caffe_FOUND)
#添加头文件搜索路径
include_directories(${Caffe_INCLUDE_DIRS})
else(Caffe_FOUND)
MESSAGE(FATAL_ERROR "Caffe library not found")
endif(Caffe_FOUND)
include_directories(../caffe_lib)
link_directories(${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
#set(test_srcs test.cpp)
#用于将当前目录下的所有源文件的名字保存在变量 test_srcs 中
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(. test_srcs)
add_executable(demo ${test_srcs})
target_link_libraries(demo classification_lib ${Caffe_LIBRARIES})
下面可以用cmake命令进行编译,为了保证项目的整洁性我建议采样外部编译
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
最终在build/lib中生成动态库,bulid/bin中生成可执行文件
看我写的辛苦求打赏啊!!!有学术讨论和指点请加微信manutdzou,注明

